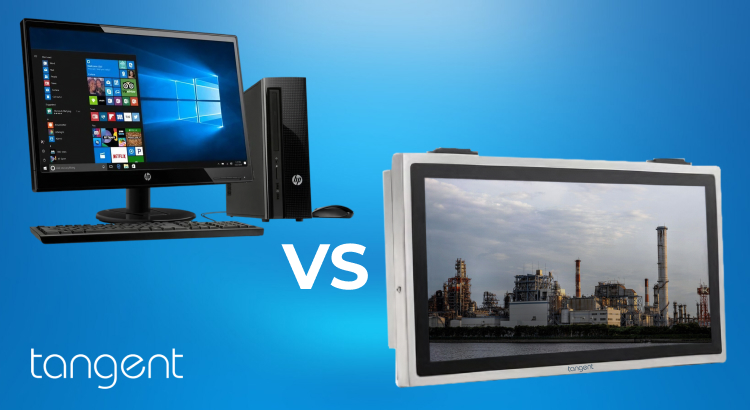
In this blog we’ll clear the air on the differences between a consumer PC and an industrial computer. You’ll have the knowledge to specify the difference between the two, as well as, determine which is proper for your application.
Understanding Industrial Computers: Key Features and Benefits for Your Business
In today’s fast-paced, technology-driven world, industrial computers are more critical than ever for a wide range of sectors. Whether you’re in manufacturing, automation, healthcare, or logistics, industrial computers (or IPCs) play a pivotal role in improving performance, reliability, and overall operational efficiency. But what makes industrial computers different from their commercial counterparts, and why should businesses invest in them?

In this blog post, we’ll explore the key differences between commercial and industrial computers, dive into the essential features of industrial computers, and highlight the benefits they bring to various industries.
What Are Industrial Computers?
Industrial computers are rugged, high-performance computing devices designed to withstand harsh environments where regular computers might falter. They are built to handle extreme temperatures, humidity, vibration, dust, and even shock. These robust systems are engineered for continuous, 24/7 operation, making them ideal for mission-critical applications in industries such as manufacturing, automation, transportation, and more.

Key Features of Industrial Computers

Durability and Ruggedness
Industrial computers are designed to endure challenging environments. Unlike commercial PCs, which are intended for use in controlled office spaces, industrial computers are often enclosed in heavy-duty casings that protect sensitive components from dust, moisture, and temperature fluctuations. Many IPCs are certified to meet IP (Ingress Protection) standards, ensuring they are dustproof and waterproof to some degree.
Extended Temperature Range
Industrial computers are engineered to operate effectively in extreme temperature conditions. While commercial PCs typically function optimally within a 10°C to 35°C (50°F to 95°F) range, industrial PCs can operate in temperature ranges as wide as -40°C to +85°C, ensuring their functionality in outdoor, factory, or industrial settings where climate control is not guaranteed.

Longevity and Reliability
One of the most critical factors for businesses using industrial computers is their longevity. These machines are built to last, with higher Mean Time Between Failures (MTBF) and support for longer lifecycle spans than commercial systems. This translates into lower total cost of ownership over time, reducing downtime and maintenance costs.
Customization and Expandability

Industrial computers are highly customizable, allowing businesses to tailor their hardware configurations to their specific needs. Whether you need more processing power, enhanced memory capacity, or additional ports, industrial computers provide the flexibility to scale and upgrade components without the need for a full system replacement.

Industrial-grade Components
Unlike commercial PCs that use standard consumer-grade components, industrial computers feature high-end components designed for long-term use in challenging conditions. These include industrial-grade processors, high-quality solid-state drives (SSDs), and more robust input/output interfaces, all engineered for superior performance and extended service life.
Key Differences Between Commercial PCs and Industrial PCs
While both commercial and industrial computers are designed to handle computing tasks, they are tailored to serve different purposes. Here are some of the most important distinctions between the two:
| Feature | Commercial PC | Industrial PC |
|---|---|---|
| Design | Consumer-friendly, sleek, and compact | Rugged and durable for harsh environments |
| Temperature Range | 10°C to 35°C (50°F to 95°F) | -40°C to +85°C or wider |
| Lifespan | Shorter lifecycle (2–3 years) | Longer lifecycle (5–10 years) |
| Expandability | Limited options for upgrades | Highly customizable and expandable |
| Applications | Office, home, and general use | Manufacturing, automation, transportation, and more |
| Cost | Lower upfront cost | Higher upfront cost, but lower long-term cost due to durability |
As shown, industrial computers excel in harsh environments and high-demand applications, while commercial PCs are more suited to everyday use in controlled settings.
Advantages of Industrial Computers for Your Business

Increased Productivity
By investing in industrial computers, businesses can ensure that their operations run smoothly without interruptions due to system failures or overheating. IPCs are designed for constant uptime, which leads to increased productivity and fewer delays in the production process.
Lower Maintenance and Downtime Costs
The high durability and reliability of industrial computers significantly reduce the need for frequent maintenance or repairs. The cost of downtime caused by system failures is reduced, and businesses can avoid the expensive repairs and replacements associated with commercial PCs that break down quickly.
Optimized for Automation
Industrial computers are central to industrial automation systems, from programmable logic controllers (PLCs) to robotic systems. Their ability to communicate with various machines and systems through a wide range of industrial protocols (such as Modbus, Profibus, EtherCAT, etc.) ensures seamless operations in automated environments.
Adaptability to Industry Needs
Every industry has its own unique set of requirements, and industrial computers can be customized to meet those needs. For instance, in healthcare, industrial computers can be configured with specialized software and hardware to run medical equipment diagnostics or track patient data in real-time. In manufacturing, industrial PCs are used to control machinery, monitor production lines, and collect data from sensors.
Long-Term Investment
Due to their longevity and scalability, industrial computers provide a long-term investment for businesses. Rather than worrying about frequent replacements, companies can depend on IPCs to handle growth and increased demand, making them cost-effective over the years.
Applications of Industrial Computers
Industrial computers are used in a wide range of industries, including:
Manufacturing:
Control and monitor production processes, machinery, and robots.

Automation:
Act as the backbone for SCADA (Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition) systems and other automation controls.
Transportation and Logistics:
Power systems for GPS tracking, vehicle monitoring, and route optimization.
Healthcare:
Operate medical devices, manage patient data, and support diagnostics.

Oil & Gas:
Monitor drilling systems, environmental conditions, and pipeline integrity.
Why Your Business Needs an Industrial Computer
In a world where operational efficiency, system reliability, and uptime are critical to success, industrial computers are an indispensable asset. Their durability, extended operational capabilities, and customizable features make them the perfect solution for industries that require rugged, reliable computing in demanding environments.

Whether you’re looking to optimize manufacturing processes, enhance automation, or simply improve your system’s resilience, an industrial computer is a wise investment for long-term success. Don’t compromise on performance—choose an industrial computer that can keep up with your business needs.
Ready to upgrade to an industrial computer? Explore our range of industrial-grade PCs designed to help you power through even the toughest environments. HERE

Call Us: 1 800 342 9388
Live Chat : Here (6:30am-3:30pm PST)
Email: sales@tangent.com
